In our previous tutorials, we have demonstrated how to implement bi-directional streaming using NodeJS. Since gRPC is just a protocol definition so it can be implemented in any possible language. So today we will demonstrate how to setup a bi-directional server using python & gRPC.
The codebase has been shared on GitHub for your convenience as follows: https://github.com/techunits/bidirectional-streaming-grpc-sample-python
In order to execute the gRPC streaming, we will need the following pip libraries as pre-requisites:
grpcio==1.39.0
grpcio-tools==1.39.0
protobuf==3.17.3
six==1.16.0
uuid==1.30The very first step to setup any gRPC communication is to create a data contract in the form of a protocol buffer file. In our demonstration, we will use a simple contract that should be able to create some resource entries to the server in the stream and expect a response in the form of a stream.
Our proto file as follows:
syntax = "proto3";
package SamplePackage;
message EntryCreateRequest {
string title = 1;
string code = 2;
string description = 3;
}
message EntryResponse {
string id = 1;
string title = 2;
string code = 3;
string description = 4;
int32 created_on = 6;
}
service SampleService {
rpc createBulkEntries(stream EntryCreateRequest) returns (stream EntryResponse) {}
}Unlike NodeJS, python classes will not able to read the proto files directly, so we have to convert the proto into native python classes. The following command will generate 2 python class files sample_pb2_grpc.py & sample_pb2.py.
python -m grpc_tools.protoc -I./proto --python_out=./proto/ --grpc_python_out=./proto/ ./proto/sample.protogRPC Streaming Server:
Now we will define our server process which will read the above classes and servicer as follows:
# import required libraries & proto defn.
import grpc
from concurrent import futures
from proto import sample_pb2_grpc
# import servicer
from servicers import SampleServiceServicer
def serve():
# initialize server with 4 workers
server = grpc.server(futures.ThreadPoolExecutor(max_workers=4))
# attach servicer method to the server
sample_pb2_grpc.add_SampleServiceServicer_to_server(SampleServiceServicer(), server)
# start the server on the port 50051
server.add_insecure_port("0.0.0.0:50051")
server.start()
print("Started gRPC server: 0.0.0.0:50051")
# server loop to keep the process running
server.wait_for_termination()
# invoke the server method
if __name__ == "__main__":
serve()The server process is having a dependency on the servicer method SampleServiceServicer defined as follows:
# import required libraries & proto defn.
from proto import sample_pb2_grpc, sample_pb2
import uuid
from datetime import datetime
class SampleServiceServicer(sample_pb2_grpc.SampleServiceServicer):
''' this servicer method will read the request from the iterator supplied
by incoming stream and send back the response in a stream
'''
def createBulkEntries(self, request_iterator, context):
entry_info = dict()
for request in request_iterator:
print(request)
##### save to database #####
# simulate the response after saving to database
entry_info = {
"id": str(uuid.uuid4()),
"title": request.title,
"code": request.code,
"description": request.description,
"created_on": round(datetime.now().timestamp())
}
# stream the response back
yield sample_pb2.EntryResponse(**entry_info)
Once we are done with the above steps, we should be able to start the server with the following command:
$ python serve.py
Started gRPC server: 0.0.0.0:50051While building the server script we have using sConnector to test and debug our script visually even before creating any client. This helps a lot for a faster development cycle. Screenshot as follows:
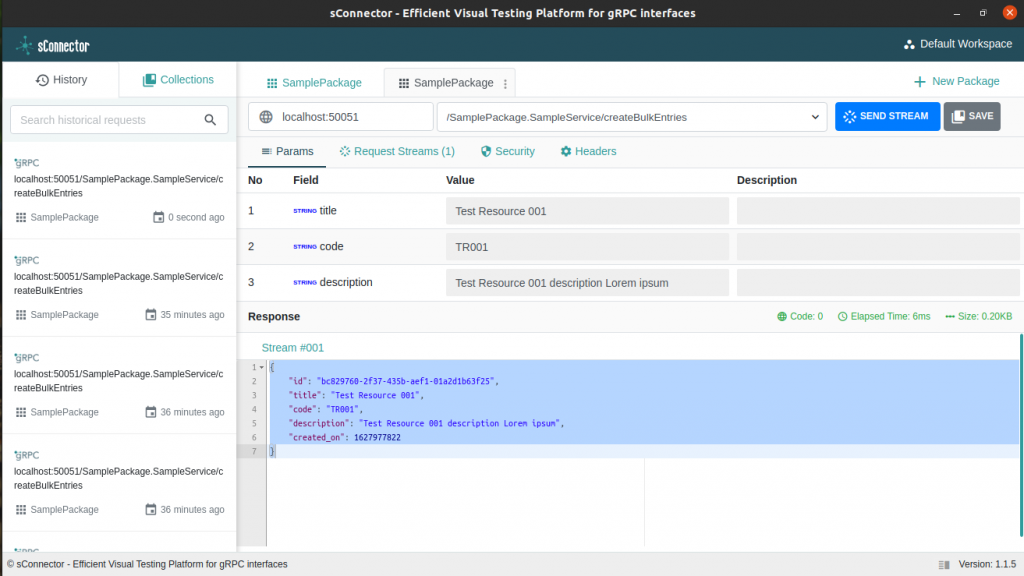
gRPC Streaming Client:
In our next tutorial, we will explain how to implement a client to connect to the streaming server and send/receive the data as follows:
How to implement bi-directional streaming using gRPC with Python (Client) – Part 2
